ENVIRONMENT
WE HAVE IMPLEMENTED TECHNOLOGIES AND SYSTEMS TO OPTIMISE WATER CONSUMPTION, ENHANCE ENERGY PRODUCTIVITY, SAFEGUARD BIODIVERSITY, MAINTAIN AIR QUALITY, AND RECYCLE & UPCYCLE WASTE.
All that Vedanta produces comes from the earth and it is thus natural that protecting and nurturing the environment is built into our business strategy and philosophy. Both our products and processes have sustainability as their central pivot.
Our products enhance longevity of other products and over time, reduce demand for natural resources. For instance, a coat of Zinc increases the longevity of metal bodies, Lead is used in the covering on wires and cables to protect them from corrosion and Silver helps in preserving food. Aluminium is one of the most recyclable metals on the planet and over the long-term, if recycled, can help reduce the need to mine virgin ore. Copper is the ubiquitous metal that powers our life. By being a strong conductor of electricity, it is one of the primary metals of an increasingly electrified society and is a key component of the renewable energy industry.
APPROACH
The Vedanta Sustainability Framework comprises comprehensive policies, standards and guidance notes, which instil systems thinking and process-oriented approach to manage environmental impacts. We have developed and publicly announced specific objectives and targets for environmental issues material to our stakeholders and to our business. We review and report our performance against these targets on an annual basis.
As part of the quantitative risk assessment and critical control development exercise, all our businesses evaluate the effectiveness of their current environmental controls and strengthen them where required. The goal is to minimise risks arising from environmental factors.
THE VEDANTA SUSTAINABILITY
FRAMEWORK ENSURES
THAT EACH OF OUR
BUSINESSES FOLLOW
THE SAME HIGH STANDARDS
OF ENVIRONMENTAL
MANAGEMENT.
WATER

Water plays a crucial role in the socio-economic development of a nation. Once considered as a free and infinite resource, water because of its growing demand, increasing scarcity, and insufficient access, has moved right up on the national and business agendas. More than ever, stakeholders now expect organisations to disclose the water risks they face.
We believe that Vedanta can help alleviate the situation by effective management of water within our operations and aiding rejuvenation of sources beyond our facilities.

|
APPROACH
Our approach to water management respects the water use rights of all stakeholders, which in turn helps strengthen our license to operate. We have instituted a water policy and a water management standard that integrates with decision-making processes for all our new and existing projects, thereby ensuring that necessary measures are in place to minimise the water footprint of our projects. We deploy a two-pronged strategy towards better water management within our operations - optimising our water consumption, and minimising the amount of fresh water we consume by reusing as much water as possible in our processes.
WATER RISK ASSESSMENT
We undertook a 'water risk assessment' exercise at 30 of our most significant business locations this year to evaluate physical, social/reputational, and regulatory risks related to water.
The risk assessment evaluated all of the processes that utilise water at our operations to understand where vulnerabilities exist.
It also looked at the internal and external perception of water risk and compared it with the water stress information available in global, public databases and site-specific measurements. The study also sought to standardise the water risk assessment approach across our Group companies so that we have a consistent methodology to evaluate this risk.
Findings
The water risk assessment found that our business operations in India (Rajasthan, Punjab, Tamil Nadu) have manifested higher degree of physical risks compared to our businesses in other locations due to their presence in high water-stress areas.
In Zambia, our operations perceive that they have higher regulatory risks due to legacy water pollution challenges. Based on these findings, we identified the areas of improvement and are in the process of developing and implementing strategies to mitigate the risks.
Measures Taken to Counter Risk
Each of our businesses has been mandated to review and put in place appropriate mitigation measures to counter water-related risks.
Hindustan Zinc has entered into a Public – Private Partnership to install and treat 20,000 m3/day of Municipal Wastewater from City of Udaipur. The water will be used for
operations at Rajpura Dariba Complex and replace part of the unit's freshwater.
KCM's Zambian operations are working with the regulatory agency and other stakeholders to mitigate water-risks.
Sterlite Copper has increased the proportion of desalinated sea-water in it's water mix.
TO FURTHER SUPPORT THE BETTER MANAGEMENT OF WATER, WE HAVE ROLLED OUT A REVISED WATER MANAGEMENT PERFORMANCE STANDARD. IN THE NEXT FISCAL YEAR, WE PLAN tO RELEASE A GUIDANCE NOTE ON WATER MANAGEMENT TO ALLOW FOR A UNIFORM IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PERFORMANCE STANDARD.
WATER PERFORMANCE DASHBOARD
Conservation and Consumption Snapshot
in cubic meters
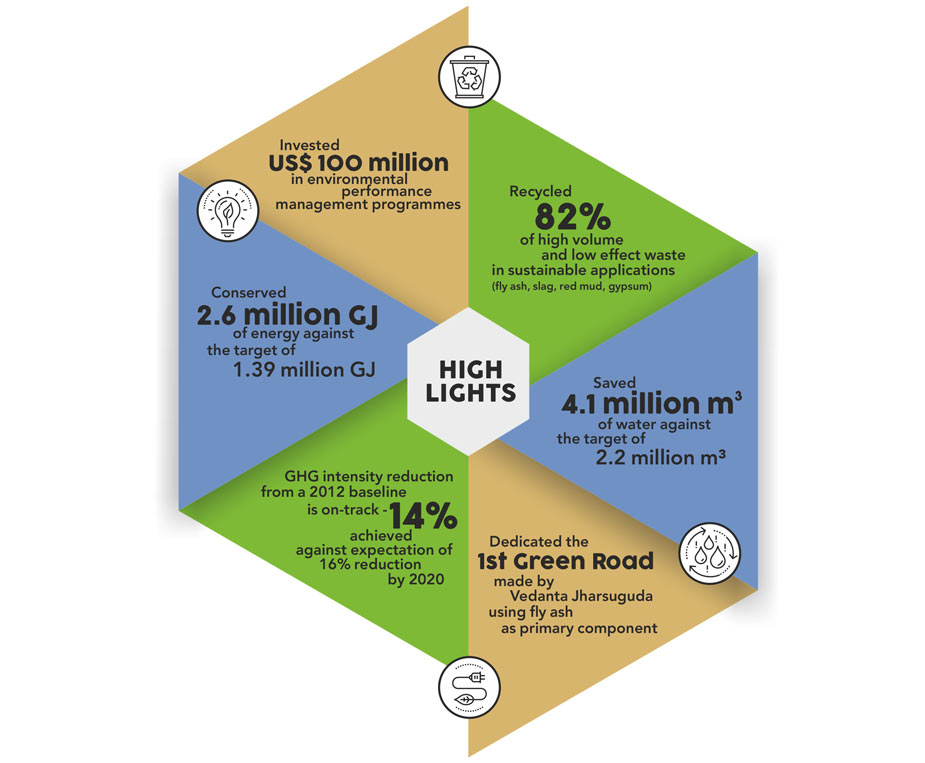
4.1 MILLION M3
WATER SAVINGS AGAINST
THE TARGETED SAVINGS OF
2.2 MILLION M3
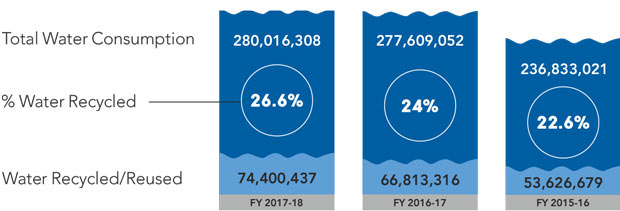
26.6%
OF WATER RECYCLED AS
COMPARED TO 24% IN THE
PREVIOUS REPORTING PERIOD

IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF DISCHARGE WATER | KCM
CHALLENGE
The Copper mines at Konkola in Zambia are some of the wettest mining operations in the world. The mining processes require ~ 350,000 m3 of water to be removed per day in order to dewater the mine shafts. Only 10% of this water is used in the processing plant and other mining operations, while the remaining 90% is discharged into a local water body – the Kakosa stream. Historically, prior to Vedanta's ownership, this discharged water had concentrations of total suspended solids (TSS) of 260 mg/l; this was significantly higher than the statutory threshold of 100mg/l prescribed by the Zambia Environmental Management Agency.

INTERVENTION
KCM embarked on a 10-year, $22 million project to improve the quality of the discharge water. Ore in KCM is mined from 'wet' pits that need to be dewatered. In the past, sediments were removed from the water that flows through the mine before being discharged to the surface. However, the concentration of suspended solids remained high, which meant that additional measures were needed to improve discharge water quality. The primary means of separating TSS from the water is via 20 settling tanks, some of which are as deep as 1,850 feet below the ground. In order to improve the efficiency of the settling tanks, four major projects were undertaken:
Refurbishment of existing underground settlers to make them more efficient
Desilting of choked drain drives, which included the removal of mud that had accumulated over the years
Procurement and installation of slurry pumps, which allowed the desludging period to be reduced from 8 months to 3 weeks
Procurement and use of flocculants to enhance settling
OUTCOME
The immediate outcomes of this project have been two-fold:
1. TSS levels are now below the statutory threshold of 100 mg/l.
2. Wear and tear on pumping infrastructure is notably reduced due
to improved water quality, which has lessened abrasive impacts.

ENERGY, EMISSIONS AND CLIMATE RELATED BUSINESS RISK
APPROACH
Vedanta's Energy and Carbon Management policy and performance standard are the guiding documents for the organisation's approach to mitigating our climate related business risk and ensuring that we minimise our energy consumption and air emissions.
We have constituted a 'Carbon Forum', which is led by the Chief Operating Officers of our businesses. The Carbon Forum has been tasked with developing and overseeing the implementation of the group's carbon mitigation approach.
Among the aspects that are managed by the Forum are discussions related to: approving the group carbon management strategy, long-term GHG emissions intensity reduction targets, alignment with investor requirements as part of the 'Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures' (TCFD), emerging regulatory risks, and carbon pricing.
ENERGY AND EMISSIONS
Climate change continues to pose an ever-present risk to the planet. India has set ambitious targets of reducing its emission intensity by 33-35% by 2030 and sourcing 40% of its electric power from non-fossil sources.
IN LINE WITH INDIA'S COMMITMENTS, AT VEDANTA, WE EXPECT TO REDUCE OUR
GHG INTENSITY BY ABOUT 16% BY 2020 FROM A 2012 BASELINE.
Companies such as Hindustan Zinc and Cairn Oil & Gas increased their investment in solar power, while other businesses made significant improvements in their process efficiencies.
During the reporting period, we were able to achieve a 14% reduction in our GHG intensity from our baseline number. Additionally, this was coupled with a 2% decline in absolute GHG emissions as compared to the previous year, which is a testament to our emission mitigation measures.

ENERGY & GHG EMISSIONS PERFORMANCE DASHBOARD
GHG Emissions – Group-wide
in tons of CO2 equivalent
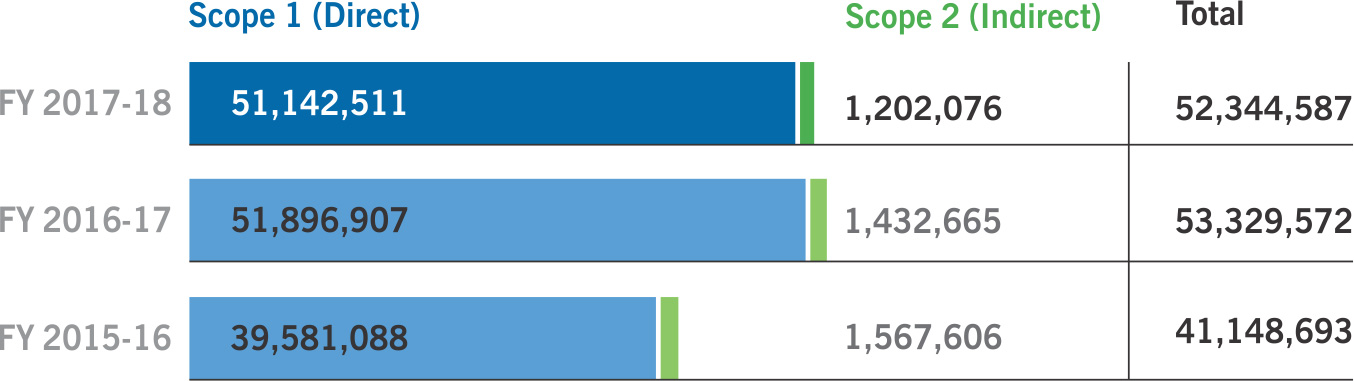
We calculate and report Greenhouse Gas (GHG) inventory i.e. Scope 1 (process emissions and other
direct emissions) and Scope 2 (purchased electricity) as defined under the World Business Council
for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) and World Resource Institute (WRI) GHG Protocol.
Energy Consumption
in million GJ
HIGHLIGHTS
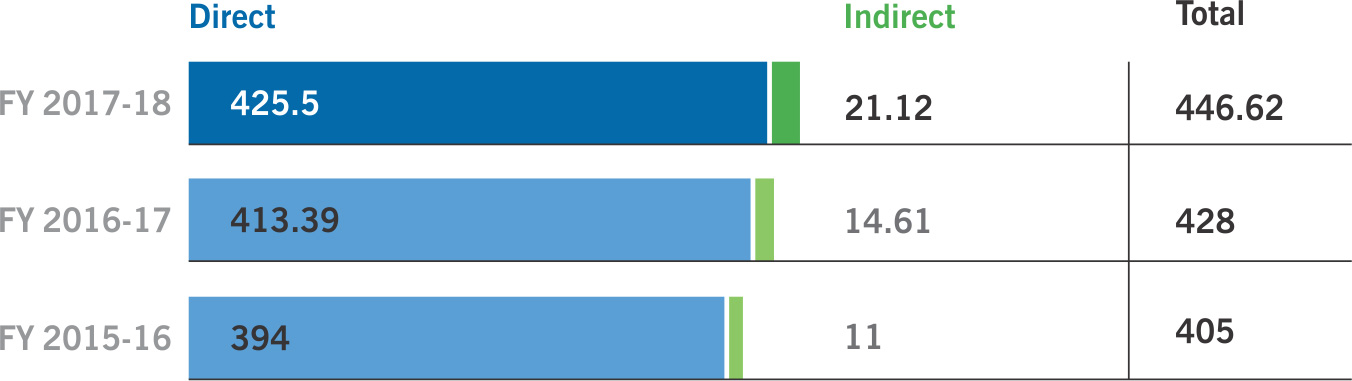
WE ACHIEVED OUR ANNUAL
ENERGY SAVING TARGET
AND SAVED ABOUT
2.6 MILLION GJ
OF ENERGY THROUGH
OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY
AND ENERGY SAVING PROJECTS
AGAINST THE TARGET OF
1.39 MILLION GJ
OF ENERGY IN THE YEAR
Our total energy consumption increased by 4% as compared to the previous year on account of increased production volumes across our businesses.
CONSERVING ENERGY
Closing the Loop to Save Energy | BALCO
To cut down on energy consumption, we introduced the closed-loop system in Rectifier Pot line - 1 & 2 pump houses. Through this new system, the process water in the rectifier is directly sent to cooling tower instead of going to the two hot well pumps for processing. The new system helped save 2.5 MWH of energy per day in each rectifier pump house. This initiative also helped reduce consumption of chemicals and water.
Changing Lights and Changing Perspectives | BALCO
We replaced conventional street lights and office lights with LED lights in BALCO's plant and township, which reduced the lighting load by 40%.
To further promote LED lights among the local community, we set up a distribution counter of energy efficient light fittings and fans under the government's Ujala & Pawan Scheme through EESL in BALCO township. We reached out to the school children and distributed 5,000 booklets, which detailed energy saving best practices.
Installation of Vapour Absorption Machine Chiller | HZL
The installation of a Vapour Absorption Machine Chiller at the Captive Power Plant of the Dariba Smelter Complex (CPP) resulted in savings of 2000 kWh/day by utilising the waste steam from the lead plant. Additionally, the Absorption Water Chiller uses water as a natural refrigerant, eliminating the need of CFC or HCFC refrigerants, which have a high global warming potential.




CLIMATE
RELATED
RISKS &
OPPORTUNITIES
THE TASK FORCE ON CLIMATE-RELATED FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES (TCFD) PUBLISHED ITS
FINAL REPORT SETTING OUT RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HELPING BUSINESSES DISCLOSE
CLIMATE-RELATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION. WE ARE STUDYING IT CLOSELY AND LOOK
FORWARD TO INCORPORATING RELEVANT FACETS INTO OUR EXISTING FRAMEWORK
OF RISK MANAGEMENT.
We are aware that climate change is triggering regulatory changes, which might affect our business operations. At Vedanta, climate related business risk sits at the Group level risk register. This enables us to review its progress at the highest level in the organisation.
We believe that resilience is the best approach we can take to safeguard our climate related business risks and are committed to work with all our stakeholders in safeguarding our business.
Carbon and water are two of our key focus areas. To keep in step with evolving national and global priorities, we have activated a group-wide carbon strategy. An internal carbon price mechanism to embed climate related financial risk in business decisions, is on the anvil.
While we continue to monitor and mitigate climate related risks, we are gearing our businesses through expansion projects, to harness climate related business opportunities. For example, copper is a key material for clean energy and we are working to increase copper production capacity at our Zambia operations to meet the expected increase in demand. We are also hopeful that our copper operations in Tasmania will start operations in the near future. We have also increased the production volumes of other metals (zinc, silver) that will be part of the renewable energy industry.

CHECKING THE HIDDEN FUGITIVE | CAIRN OIL & GAS
CHALLENGE
In the oil & gas industry, fugitive emissions can often constitute a significant proportion of the company's GHG emissions.
These invisible but accounted for emissions are not only a waste of resources, but also have a high global warming potential (GWP), as they are primarily methane emissions, which are 23 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of GWP. Excessive, unchecked fugitive emissions also pose a potential fire hazard.
INTERVENTION
Cairn Oil & Gas, along with an independent external expert, conducted a fugitive emissions study, based on the US EPA Method 21 approach, for its Rajasthan operations.
A leak detection and repair (LDAR) programme was carried out to check for emission leaks from process equipment. All joints such as valves, connectors, pumps, sampling connections, compressors, pressure relief devices and open-ended lines in the process plant and well pads were monitored.
OUTCOME
The Findings Were Surprisingly Positive, Fugitive Emissions Accounted For Only 0.011% Of The Total Ghg Emissions Of The Process And Well Pad Areas; Significantly Lower Than The 13% Correction Factor That Was Being Applied To Account For The Unmeasured Emissions.
These numbers also compared favourably with fugitive emission ranges found in North American oil and gas installations. This study highlights the excellent asset management and upkeep of facilities in our oil and gas business.


UNLOCKING PIPELINE CAPACITY TO REDUCE EMISSIONS | CAIRN OIL & GAS
CHALLENGE
At Raageshwari Gas terminal, wet gas received from well pads is separated as gas, hydrocarbon condensate and water.
Separated condensate is transferred to the Mangala Processing Terminal,
150 km away, through a 4-inch pipeline. The carrying capacity of this pipeline was limited to 3,000 barrels per day and to manage additional condensate production, trucking was the only solution.
INTERVENTION
Drag Reducing Agent was introduced in the pipeline to reduce turbulence.
This diminished the drag force between pipeline wall and condensate resulting in unlocking of additional capacity.

OUTCOME
The injection of drag reduction agent helped:
Increase flow capacity of the
pipeline from 3,000 barrels per
day to 5,000 barrels per day
reducing trucking requirements
Reduction of risks involved in daily
transportation of hydrocarbon
condensate
Reduced GHG emissions by around
900 tCO2 equivalent per year
BIODIVERSITY
VEDANTA STRIVES TO PREVENT ANY ADVERSE IMPACTS ON BIODIVERSITY. WE MANAGE
AND USE LAND ACROSS THE ENTIRE PROJECT LIFE-CYCLE IN A MANNER THAT BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION NEEDS ARE INTEGRATED WITH BUSINESS NEEDS.
APPROACH
We have adopted a 'Biodiversity Policy and Management Standard' in line with international standards and guidelines of IFC. It is an integral part of Vedanta's commitment to sustainable development.
We also follow International Finance Corporation (IFC) guidelines and ICMM mitigation hierarchy - an internationally recognised approach designed to help limit, as far as possible, the impacts of development projects on biodiversity and ecosystem services.
BIODIVERSITY MANAGEMENT HAS BEEN MADE INTEGRAL IN ALL OUR PROJECTS ACROSS ALL THREE PHASES - THE DESIGN STAGE,
THE OPERATION PHASE AND DURING THE POST CLOSURE PHASE.
We conduct Environmental Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) of new projects or major expansions to understand the presence of critical biodiversity attributes before commencing work on a new project.
Sites that have the potential for having a significant impact on the biodiversity of an area have developed a Biodiversity Management Plan (BMP) to mitigate the impact of our operations.
As of FY 2017-18, more than 80% of our sites have re-evaluated their BMP and are in the process of developing plans to mitigate any impact.
Even after the project site closure we continue our efforts to restore and rejuvenate the site by developing degraded land into green zones.

TURNING DEGRADED LANDS INTO GREEN ZONES | KCM
CHALLENGE
Over 70 years of mining operation in Zambia have resulted in the degradation of large tracts of land by mine waste that contains elevated levels of heavy metals and low levels of plant nutrients, beneficial soil micro-organisms and poor water retention capabilities. Weak consolidation, pollution and low fertility mean that the land is not useful for conventional agriculture. Plus, wind and water erosion of sediments pose a serious potential threat to the environment and human health.
INTERVENTION
KCM and BetterWorld Energy Ltd. pioneered a phyto-stabilisation and phyto-remediation approach for the regeneration of disused copper-tailings-storage facilities and overburden. In a pilot programme, 3,000 nitrogen fixing, drought and salinity tolerant, non-edible oil-seed Pongamia pinnata were planted on 5 hectares of land at TD2 Nchanga Mine Site, Chingola. Tree survival rates after 1 year exceed 99%.
OUTCOME
The growing trees and intercrops are solving several critical environmental and employment issues such as:
Reducing wind and water erosion and river sedimentation as roots bind the soil.
Phytostabilisation of heavy metals in their roots system and in the soil through strong binding with organic matter that is built up in the soil from leaf fall.
The land regeneration approach is providing jobs in post-mining and peri-urban towns of Zambia not
just during the land regeneration process but
also beyond.


PROTECTING THE WILDERNESS WHERE WILDLIFE LIVES | CAIRN OIL & GAS
CHALLENGE
Deserts are usually stereotyped as lifeless wastelands, low in diversity of both plants and animals. But the Rajasthan block of our oil & gas business is one of the exceptions. It is home to 300 flora and fauna species, which are supported by a good distribution of waterbodies. However, due to low rainfall, recurring drought-like conditions, and depleting ground water table, water availability beyond the monsoon becomes a challenge.
INTERVENTION
Pond Development
Cairn developed a pond 'Gajlar' in the reserved forest area of Gangali in Barmer district with the purpose of making water available to the wild animals throughout the year. Water to this pond is supplied from a dedicated bore-well equipped with a solar power operated 5-hp water pump.
The habitat in Gangali is vastly different from the habitats observed in the block area and it is known to support wildlife such as Indian gazelle and many other wild animals and birds.
De-silting of Water Bodies
Cairn, under its CSR projects, carried out de-silting of seven water bodies with cumulative storage of ~10 lakh cum of rainwater, which is available during post-monsoon period or throughout the year in some cases.
Ambulance for Injured Wild Animals
Cairn handed over to the forest department a dedicated vehicle with necessary tools and tackles to transport injured and dead wild animals.
Shelterbelt Plantation on Community Land
Cairn in collaboration with the local forest department developed ~84 ha of greenbelt cover on community land in Barmer and Jalore districts. These greenbelts provide good shelter for wild animals.
OUTCOME
A significant number and variety of wild
animals and bird species are thriving
in this area since the commissioning
of the pond in June 2017

AIR QUALITY
APPROACH
VEDANTA OPERATES WITH
A PHILOSOPHY OF 'ZERO HARM'
AND MANAGE EMISSIONS TO
AIR FROM POINT SOURCES
AND FROM PROCESS
ACTIVITIES ASSOCIATED
WITH COMBUSTION.
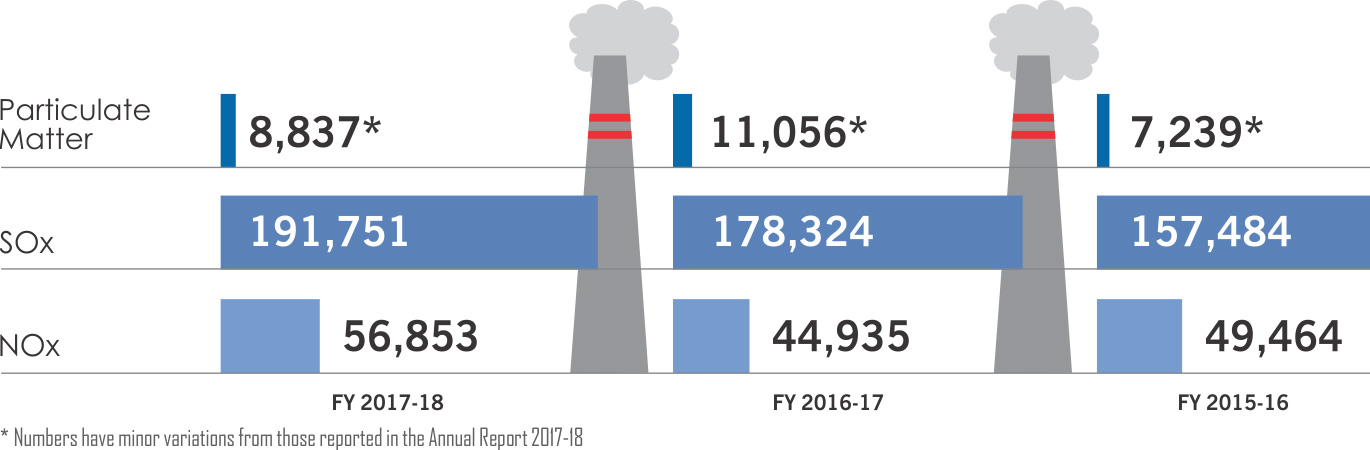
As part of our ambient air quality monitoring process, we monitor Particulate Matter (PM) and SOx. We also monitor lead, fluoride and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) emissions from our operations as applicable. We do not record ozone-depleting emissions as this is not a material issue to our operations.
New stringent norms for stack emissions - SOx, NOx, Particulate Matter and Water Efficiency from independent and captive power plants in India came into effect in December 2017. Most of our operations meet the NOx and Particulate Matter norms or are in the process of meeting them, but the challenge for us is to meet the new SOx norms considering our site layout and effectiveness of available technologies in abating overall pollution and environmental impact.
STACK EMISSIONS SNAPSHOT in MT
WASTE
EXPLORATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES PROVIDES GREAT ECONOMIC OPPORTUNITIES FOR RESOURCE-RICH COUNTRIES.
BUT IT ALSO GENERATES LARGE QUANTUM OF WASTE, WHICH NEEDS TO BE MANAGED WELL.
APPROACH
In accordance with our Resource Use and Waste Management Technical Standard, we follow the waste management hierarchy of first decreasing the waste, quantitatively as well as qualitatively by reducing its toxicity, and then recovering and recycling where possible, either by ourselves or through authorised recyclers. The last stage is disposal in landfill or by incineration, using authorised, licenced and secured landfills. We aim to remain environmentally friendly across all the stages.
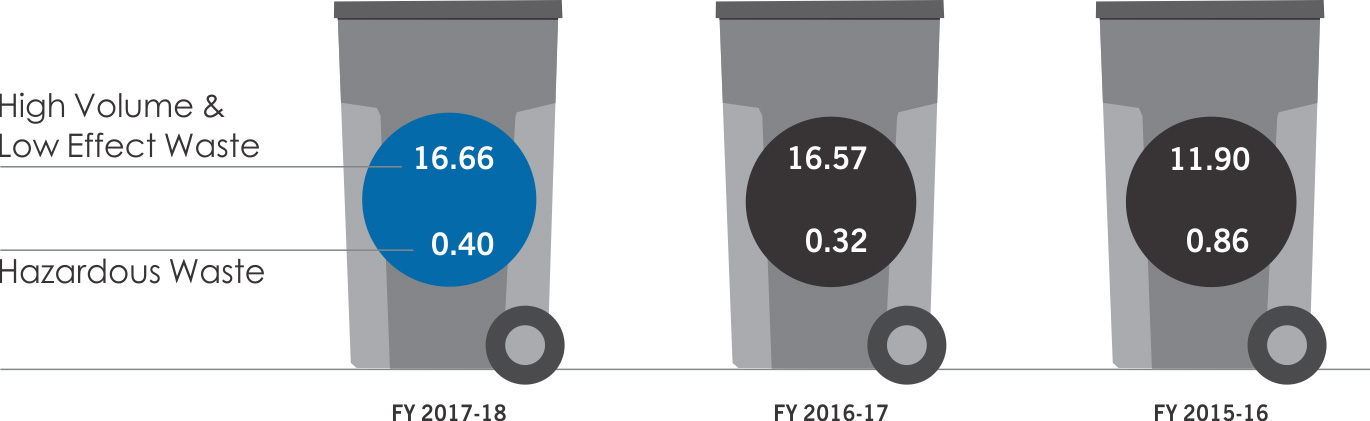
The major wastes generated from our operations can be segmented into two categories:
Hazardous waste which includes used/spent oil, waste refractories, aluminium dross, spent pot lining and residual sludge from smelters
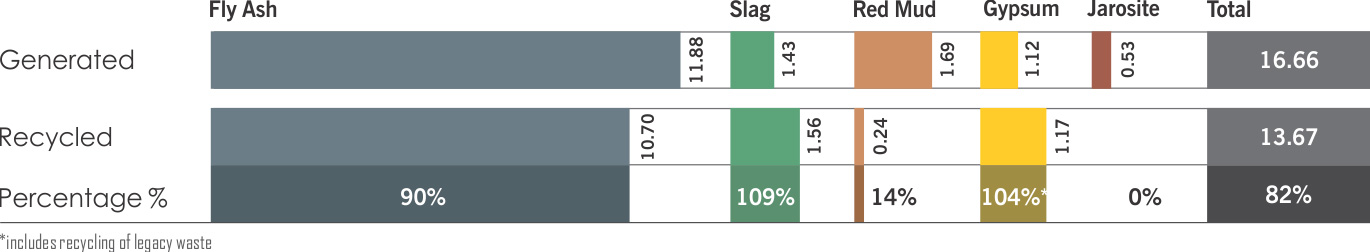
High-Volume Low-Effect waste which includes fly ash, slag, red mud, gypsum, and jarosite

WASTE PERFORMANCE DASHBOARD
Waste Generation & Recycle Snapshot
in million MT
High-Volume & Low-Effect Waste Management
in million MT
HIGHLIGHTS
REUSED/RECYCLED
~61%
OF OUR HAZARDOUS WASTE
82%
OF OUR HIGH-VOLUME AND
LOW-EFFECT WASTE IN
SUSTAINABLE APPLICATIONS
TOTAL FLY ASH UTILISATION INCREASED TO
90% IN FY 2017-18
FROM 53% IN THE PREVIOUS YEAR AS WE DEPLOYED
IT TO REPAIR THE TAILINGS DAM AND ASH-DYKE
WALLS AT JHARSUGUDA AND BALCO
TAILINGS DAMS
Tailings dams are considered a significant HSE risk and have been part of the Group Risk Register since FY 2015-16. A breach in the dam is a loss of containment event, which results in the spillage of accumulated wastes that can pollute the soil and damage property due to a 'flood' event. It therefore becomes imperative that their integrity is maintained.
Last year we conducted a tailings dam risk assessment study at nine dams across our businesses that would have significant impacts in case of failure. In two out of these nine dams, an additional dam-break analysis was conducted due to the condition of their structures.
However, as responses to the findings were being designed, one of the dams - located at our Aluminium & Power Business in Jharsuguda - experienced a breach in the wall of the ash dyke.
This resulted in a spillage of the contained fly ash onto an adjacent plot of land, majority of which belongs to Vedanta.
In anticipation of a lack of storage space for newly produced fly ash, the regulator (Odisha State Pollution Control Board) imposed partial restrictions on operation of our power plants. This restriction was progressively lifted as storage space became available. Corrective actions have been taken at both the critical structures where the dam-break analysis was conducted.
We also experienced a minor overflow of the ash dyke at BALCO. However, the incident did not result in any significant environment, health and safety, and social impacts.
These incidents have raised the urgency with the organisation on potential failures in the future.
A comprehensive plan to eliminate this risk has been undertaken.
A crucial first step is the decision to further review all our dams globally so that we can ensure they are all designed, constructed and managed consistently in line with global practices.
We have engaged an experienced third party to conduct this evaluation. We have also rolled out the 'Vedanta Tailings Management Standard',
to ensure that we have consistent dam management practices across all Group companies.
The assessment was completed in March 2018 and the findings have been shared with our Group executive committee and risk committee. The businesses are in the process of addressing issues reported from the assessment.
We have also established a regular third-party inspection to critical locations and appointed a global expert to provide long term advice and monitoring, covering the design, construction and operation of each
storage dam.

